Stomach cancer
Stomach cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, arises from the cells lining the stomach. It often develops gradually over many years, starting with precancerous changes in the stomach lining. Symptoms may not manifest until the cancer reaches an advanced stage, making early detection challenging. Risk factors include age, diet, smoking, and certain infections.
Treatment options depend on the stage and may include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Despite advancements in treatment, stomach cancer remains a significant global health concern, emphasizing the importance of prevention and early intervention strategies.
Risk Factors
- Helicobacter pylori infection: This bacterium is a major risk factor for stomach cancer.
- Diet: Consumption of smoked, pickled, or salty foods, and low intake of fruits and vegetables can increase the risk.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption.
Symptoms
- Early stages may be asymptomatic.
- Symptoms may include persistent indigestion, stomach pain or discomfort, nausea, vomiting, unintentional weight loss, blood in the stool, and difficulty swallowing.
Diagnosis
- Endoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the stomach to examine it visually.
- Biopsy: Tissue samples are taken from suspicious areas for examination under a microscope to confirm cancer.
- Imaging tests: CT scans, PET scans, and MRI scans may be used to determine the extent of the cancer.
Treatment
- Surgery: Removal of part or all of the stomach (partial or total gastrectomy) may be necessary, along with nearby lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs are used to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors.
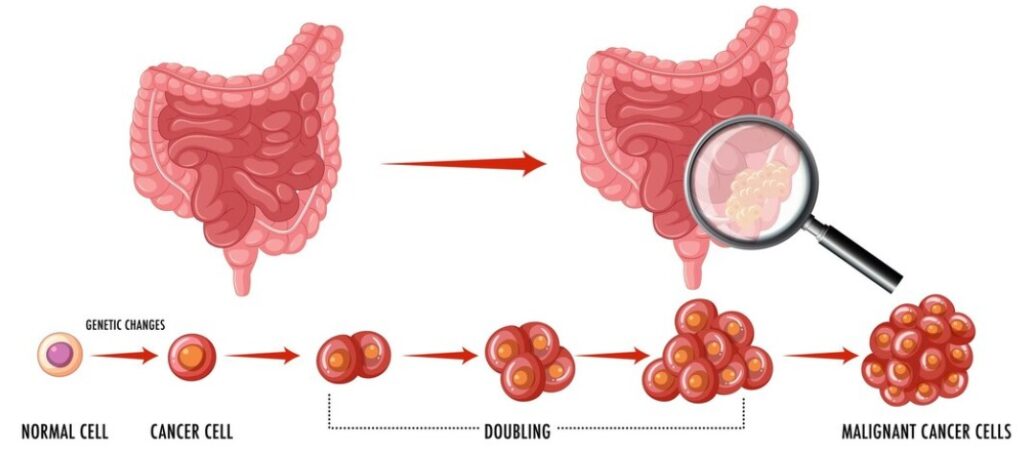
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, develops in the lining of the stomach and is often detected at advanced stages. For the best gastric oncologist in Dehradun, consider consulting Dr. Ajeet Tiwari is renowned for his expertise in treating stomach cancer and providing personalized care to patients, ensuring comprehensive evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and tailored treatment plans to optimize outcomes.
